

Hoàng Duy Phong
Giới thiệu về bản thân


































I agree that technology has significantly helped students to study better. Here are some key points:
- Access to Information: Technology provides students with easy access to a vast range of information and resources online, like educational websites, research papers, e-books, and tutorials. This makes learning more comprehensive and convenient.
- Interactive Learning: Tools such as educational apps, videos, and games make learning more engaging. For example, platforms like Khan Academy or Duolingo offer interactive lessons that can help students understand complex topics in a fun way.
- Personalized Learning: Technology allows for adaptive learning platforms that can cater to individual needs, allowing students to learn at their own pace. Tools like quizzes and assessments help identify areas where students need improvement, providing them with personalized study plans.
- Collaboration and Communication: With online discussion forums, group chats, and video calls, students can collaborate with peers and teachers, even from different parts of the world. This can foster a more collaborative learning environment.
- Time Management and Organization: Students can use apps for task management, reminders, and calendars, which can help them stay organized and better manage their study schedules.
I agree that technology has significantly helped students to study better. Here are some key points:
Access to Information: Technology provides students with easy access to a vast range of information and resources online, like educational websites, research papers, e-books, and tutorials. This makes learning more comprehensive and convenient.Interactive Learning: Tools such as educational apps, videos, and games make learning more engaging. For example, platforms like Khan Academy or Duolingo offer interactive lessons that can help students understand complex topics in a fun way.Personalized Learning: Technology allows for adaptive learning platforms that can cater to individual needs, allowing students to learn at their own pace. Tools like quizzes and assessments help identify areas where students need improvement, providing them with personalized study plans.Collaboration and Communication: With online discussion forums, group chats, and video calls, students can collaborate with peers and teachers, even from different parts of the world. This can foster a more collaborative learning environment.Time Management and Organization: Students can use apps for task management, reminders, and calendars, which can help them stay organized and better manage their study schedules.I agree that technology has significantly helped students to study better. Here are some key points:
- Access to Information: Technology provides students with easy access to a vast range of information and resources online, like educational websites, research papers, e-books, and tutorials. This makes learning more comprehensive and convenient.
- Interactive Learning: Tools such as educational apps, videos, and games make learning more engaging. For example, platforms like Khan Academy or Duolingo offer interactive lessons that can help students understand complex topics in a fun way.
- Personalized Learning: Technology allows for adaptive learning platforms that can cater to individual needs, allowing students to learn at their own pace. Tools like quizzes and assessments help identify areas where students need improvement, providing them with personalized study plans.
- Collaboration and Communication: With online discussion forums, group chats, and video calls, students can collaborate with peers and teachers, even from different parts of the world. This can foster a more collaborative learning environment.
- Time Management and Organization: Students can use apps for task management, reminders, and calendars, which can help them stay organized and better manage their study schedules.
- Hoa lưỡng tính là loại hoa có cả bộ phận sinh dục cái (nhụy) và bộ phận sinh dục đực (nhị), tức là cả hai bộ phận sinh sản trong cùng một hoa.
- Hoa đơn tính là hoa chỉ có một trong hai bộ phận sinh dục, hoặc chỉ có nhị (đực) hoặc chỉ có nhụy (cái)
xyOABM
a) Điểm A thuộc tia Ox nên tia OA cũng chính là tia Ox.
Điểm B thuộc tia Oy nên tia OB cũng chính là tia Oy.
Vì hai tia Ox và Oy đối nhau nên hai tia OA và OB đối nhau.
Suy ra điểm O nằm giữa hai điểm A và B.
b) Vì điểm M nằm giữa O và A nên tia OM cũng chính là tia OA.
Mà hai tia OA và OB đối nhau.
Do đó hai tia OM và OB đối nhau.
Suy ra điểm O nằm giữa hai điểm B và M.
c) Điểm O nằm giữa A và B suy ra: AO + OB = AB hay 3 + OB = 6.
Do đó OB = 3 (cm)
Vì OA = 3 cm; OB = 3 cm mà O nằm giữa A và B nên O là trung điểm của đoạn thẳng AB.
xyOABM
a) Điểm A thuộc tia Ox nên tia OA cũng chính là tia Ox.
Điểm B thuộc tia Oy nên tia OB cũng chính là tia Oy.
Vì hai tia Ox và Oy đối nhau nên hai tia OA và OB đối nhau.
Suy ra điểm O nằm giữa hai điểm A và B.
b) Vì điểm M nằm giữa O và A nên tia OM cũng chính là tia OA.
Mà hai tia OA và OB đối nhau.
Do đó hai tia OM và OB đối nhau.
Suy ra điểm O nằm giữa hai điểm B và M.
c) Điểm O nằm giữa A và B suy ra: AO + OB = AB hay 3 + OB = 6.
Do đó OB = 3 (cm)
Vì OA = 3 cm; OB = 3 cm mà O nằm giữa A và B nên O là trung điểm của đoạn thẳng AB.
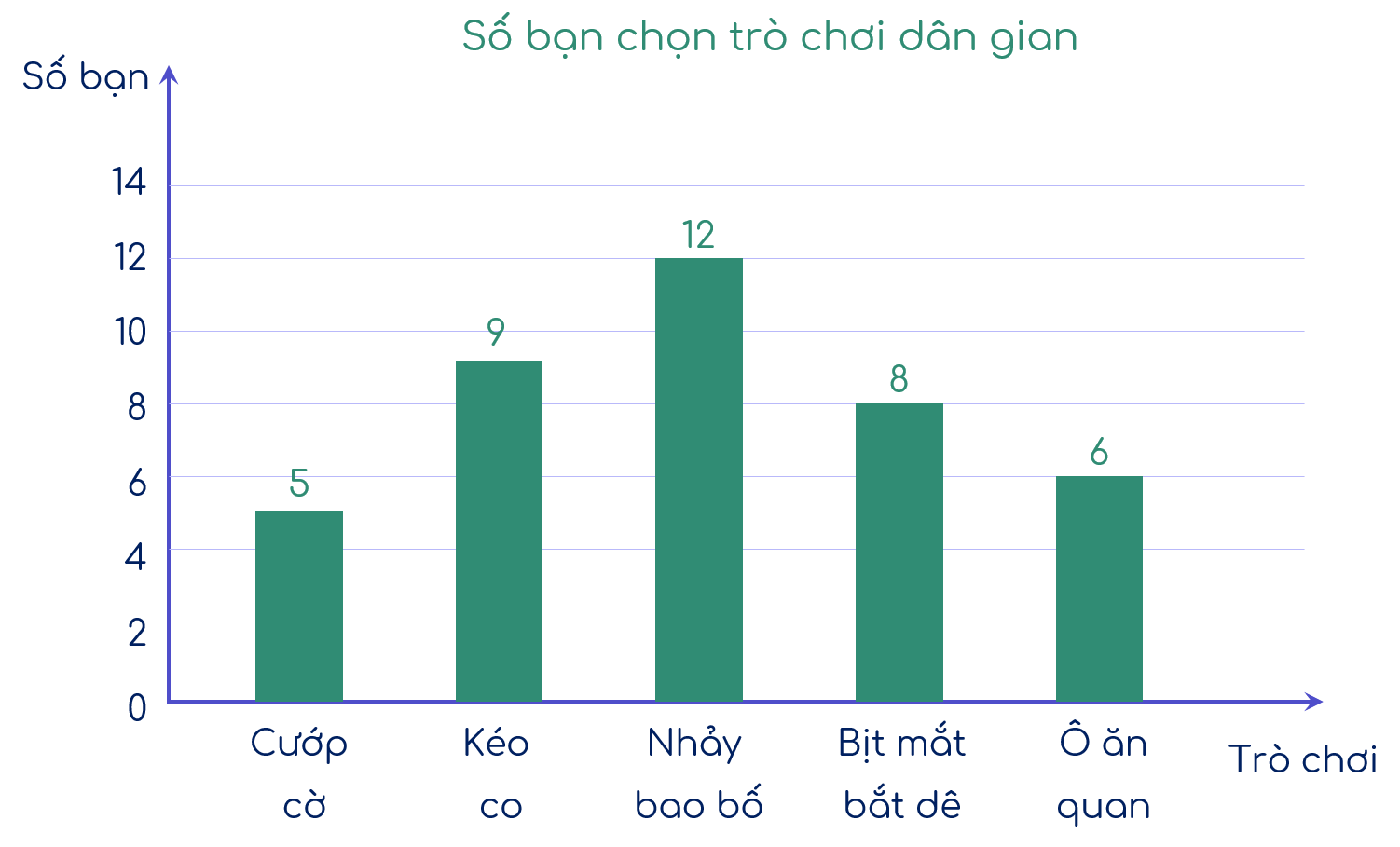
Đổi \(25 \%\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\).
Ta có \(28\)m vải còn lại ứng với:
\(1 - \frac{1}{3} = \frac{2}{3}\) (số mét vải còn lại sau ngày thứ nhất).
Sau ngày thứ nhất người đó bán còn lại số mét vải là:
\(28 : \frac{2}{3} = 42\) (m)
Số mét vải ban đầu là:
\(\left(\right. 42 + 15 \left.\right) : \left(\right. 1 - \frac{1}{4} \left.\right) = 57 : \frac{3}{4} = 76\) (m).
a) \(\frac{3}{8} - \frac{1}{6} x\) \(= \frac{1}{4}\)
\(\frac{3}{8} - \frac{1}{6} x\) | \(= \frac{1}{4}\) |
\(\frac{1}{6} x\) | \(= \frac{3}{8} - \frac{2}{8}\) |
\(\frac{1}{6} x\) | \(= \frac{1}{8}\) |
\(x\) | \(= \frac{1}{8} : \frac{1}{6}\) |
\(x\) | \(= \frac{3}{4}\)
|
Vậy \(x = \frac{3}{4}\).
b) \(\left(\left(\right. x - 1 \left.\right)\right)^{2} = \frac{1}{4}\)
Suy ra \(\left[\right. & \left(\left(\right. x - 1 \left.\right)\right)^{2} = \left(\left(\right. \frac{1}{2} \left.\right)\right)^{2} \\ & \left(\left(\right. x - 1 \left.\right)\right)^{2} = \left(\left(\right. \frac{- 1}{2} \left.\right)\right)^{2}\) hay \(\left[\right. & x - 1 = \frac{1}{2} \&\text{nbsp}; \\ & x - 1 = \frac{- 1}{2} \&\text{nbsp};\)
\(\left[\right. & x = \frac{1}{2} + 1 \&\text{nbsp}; \\ & x = \frac{- 1}{2} + 1 \&\text{nbsp};\) suy ra \(\left[\right. & x = \frac{3}{2} \&\text{nbsp}; \\ & x = \frac{1}{2} \&\text{nbsp};\)
Vậy \(x \in \left{\right. \frac{3}{2} ; \frac{1}{2} \left.\right}\).
c) \(\left(\right. x - \frac{- 1}{2} \left.\right) . \left(\right. x + \frac{1}{3} \left.\right) = 0\).
Suy ra \(\left[\right. & x - \frac{- 1}{2} = 0 \\ & x + \frac{1}{3} = 0\) hay \(\left[\right. & x = \frac{- 1}{2} \&\text{nbsp}; \\ & x = \frac{- 1}{3} \&\text{nbsp};\)
Vậy \(x \in \left{\right. \frac{- 1}{2} ; \frac{- 1}{3} \left.\right}\).
a) \(\frac{1}{3} + \frac{3}{4} - \frac{5}{6}\)
\(= \frac{4}{12} + \frac{9}{12} - \frac{10}{12}\)
\(= \frac{4 + 9 - 10}{12}\)
\(= \frac{3}{12}\)
\(= \frac{1}{4}\).
b) \(\frac{- 2}{3} + \frac{6}{5} : \frac{2}{3} - \frac{2}{15}\)
\(= \frac{- 2}{3} + \frac{6}{5} . \frac{3}{2} - \frac{2}{15}\)
\(= \frac{- 2}{3} + \frac{18}{10} - \frac{2}{15}\)
\(= \frac{- 2}{3} + \frac{9}{5} - \frac{2}{15}\)
\(= \frac{- 10}{15} + \frac{27}{15} - \frac{2}{15}\)
\(= \frac{15}{15} = 1\).
c) \(\frac{- 3}{7} + \frac{5}{13} + \frac{- 4}{7}\)
\(= \left(\right. \frac{- 3}{7} + \frac{- 4}{7} \left.\right) + \frac{5}{13}\)
\(= \frac{- 7}{7} + \frac{5}{13}\)
\(= - 1 + \frac{5}{13}\)
\(= \frac{- 8}{13}\).
d) \(\frac{12}{19} + \frac{- 8}{13} - \frac{12}{19} + \frac{5}{- 13} + 2\)
\(= \frac{12}{19} + \frac{- 8}{13} - \frac{12}{19} + \frac{- 5}{13} + 2\)
\(= \left(\right. \frac{12}{19} - \frac{12}{19} \left.\right) + \left(\right. \frac{- 8}{13} + \frac{- 5}{13} \left.\right) + 2\)
\(= 0 + \frac{- 13}{13} + 2\)
\(= 1\).